Testnet vs Mainnet: Why Testing is Essential For Blockchains and Smart Contracts

Blockchains and smart contracts must be impervious to hacks.
A report from ImmuneFi found that 3.7 BILLION USD was lost due to hacks in 2022.
This all could have been avoided if developers spent more time on quality assurance in a testnet phase before launching mainnet.
Understanding Testnet vs Mainnet
A testnet is a network used by developers to test their blockchain or cryptocurrency applications without using real tokens or real-world transactions. Testnets are designed to mimic the functionalities of the mainnet, but with some important differences, such as using test tokens that have no real value, shorter block times, and reduced mining difficulty. Testnets allow developers to experiment and test their applications in a safe and controlled environment before deploying them to the mainnet.
On the other hand, a mainnet is the live and operational version of a blockchain or cryptocurrency network. It is the network where real tokens are used for transactions and real-world applications are deployed. The mainnet is the ultimate goal for developers, as it is the network that will be used by real users and where real value will be transferred.
Both mainnet and testnet play an important role in blockchain development. Mainnets signify the maturity of the projects as they represent viable products ready for public use.
Yet, it’s worth highlighting the importance of test networks, too.
In contrast to traditional development processes, blockchain projects are usually devoid of central control units where developers can easily fix bugs and patch vulnerabilities.
Testnets enable testing the pieces of code in a safe environment without risking real funds. They help project teams to reveal potential bugs before the launch and increase the engagement of their communities. All-in-all, testnets are just as important as mainnets and play a crucial role in blockchain development.
What Is A Blockchain Testnet?
A testnet, or a test network, is an experimental replica of a live blockchain. With its help, one can create, test, and modify different features without affecting the actual blockchain.
In fact, it represents a sandbox environment for testing new features in a risk-free manner with the final goal of finding the most stable version of a separate feature or the whole product.
A test network is a great solution for locating and fixing bugs that can have a negative effect on decentralized applications at later stages. At this, it is particularly useful for developers, testers, security auditors, and other specialists engaged with blockchain development.
Key Characteristics Of A Testnet
Although a testnet is almost an identical copy of a live mainnet, there are still some core aspects that make it different. Thus, it comes with the following key features:
- Transactions on a test network are not recorded to the public blockchain. Testnets make it possible to execute pieces of code in a safe environment. No activities performed on a testnet leave any traces on the mainnet.
- The native coin of a testnet has no value outside the network. Within the testnet, it’s possible to generate as many tokens as you need. However, they are useless anywhere outside of the test network. One may try to send these tokens somewhere else, but they will simply burn in the process. And vice versa, the tokens from a working mainnet can’t be sent to a testnet either.
- The difficulty of mining doesn’t increase on the testnet. This feature is particularly useful for PoW-based blockchains. The algorithm regulating the difficulty of new coins’ creation is fixed. Thus, it helps to simplify the testing processes but at the same time devalues testnet tokens.
- A testnet has its own genesis block. A genesis block represents the very first block of a blockchain network. Both mainnet and testnet begin their existence at different genesis blocks.
Examples Of Testnets
Ethereum features the following testnets:
- Kovan
- Rinkeby
- Sokol
- Görli
- Ropsten
All other popular blockchains like Solana and Binance Smart Chain have their own versions of testnets as well.
Key Use Cases Of A Testnet
Immutability is one of the key distinctive features of blockchain. In practice, it means that it is impossible to change the code once it goes live on the network. Thus, if the code contains bugs, it will be practically impossible to fix them. At the same time, when discovered by hackers, these bugs can result in severe money losses.
Workarounds for this problem exist, of course, but in most cases, they are quite complicated.
The key use cases of testnets include the following options:
- Development in safe testnet environments. Testnets enable developers to test smart contracts in a secure environment, discover critical bugs and eliminate them.
- No disruption for the mainnet. Developers struggle to create blockchains that would be secure, decentralized, and scalable (see Blockchain Trilemma). Testnets enable them to test all the changes without disrupting the final products.
- Free tests. With testnets, developers can test their products without investing any real money. Thus, a test network represents some sort of a free trial with an unlimited testing period.
- Bug detection. Testnets make it possible to reveal and fix bugs in the code before releasing it to the main network. Combined with third-party auditing services, this may significantly increase the security of the future product.
- Community engagement. Blockchain projects with huge community support often rely on the testnets to drive users’ engagement further. They announce various bug discovery competitions and reward those who help them find any issues before the release of the final product.
What Is A Blockchain Mainnet?
A main network, or mainnet for short, is a fully developed and functional platform. On the mainnet, users can interact with each other, send and receive tokens and exchange real value.
The mainnet records all transactions, verifies their authenticity and broadcasts them to the distributed ledger. At this, transactions bear real value while the mainnet itself signifies the maturity of the project.
Key Characteristics Of A Mainnet
As a fully functional blockchain, a mainnet comes with the following features:
- Mainnet represents an independent blockchain. It runs totally by itself and doesn’t rely on any external infrastructure.
- Users perform real activities. The activities they execute have an impact on the market price of the underlying assets. In fact, all operations that take place on the mainnet have economic value and thus contribute to the security of this network. In addition, mainnets require their participants to pay transaction fees that have real value, too.
- Network validators get real rewards for their activities. Miners who support the mainnet and verify transactions get real cryptocurrencies for their work.
- When a mainnet gets updated or revised, it impacts the price of the underlying assets. Those developers who strive to make their products successful, constantly work on fixing existing bugs and adding new features. Significant updates usually make the community excited and push the asset price upward.
For example, Ethereum's price went steadily upward after the network switched to the proof-of-stake consensus mechanism at the end of November 2020:
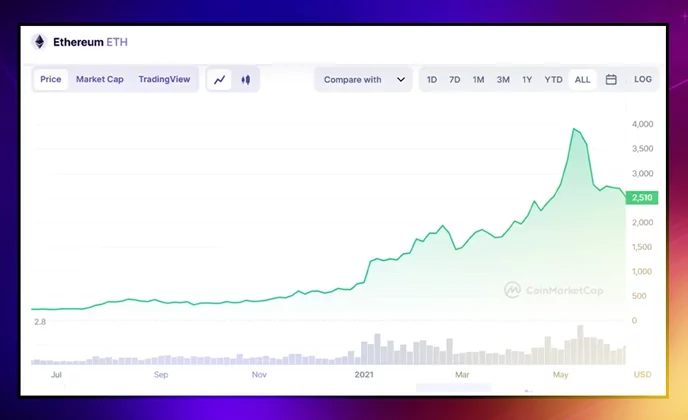
CoinMarketCap: ETH price started growing exponentially after the project had reached another major milestone
Examples Of The Popular Mainnets:
Ethereum represents one of the most popular mainnets available in the market so far. Other popular solutions include:
- Polygon
- Solana
- Binance Smart Chain
- Tezos
- TRON
Key Use Cases Of A Mainnet
Mainnet is a serious step in the development process of any blockchain project. At this, it comes with the following key use cases:
- Credibility. In most situations, development teams make the code of their products public. The release of an open source blockchain contributes to community trust and increases the credibility of the projects.
- Actual transactions. Mainnets enable users to transfer real funds in a non-custodial manner.
- A proof of development. Mainnets serve as a verification of the real work performed by developers. They represent a viable product and signify that the projects can be trusted.
Join The Leading Crypto Channel
JOINDisclaimer:Please note that nothing on this website constitutes financial advice. Whilst every effort has been made to ensure that the information provided on this website is accurate, individuals must not rely on this information to make a financial or investment decision. Before making any decision, we strongly recommend you consult a qualified professional who should take into account your specific investment objectives, financial situation and individual needs.

Kate
Kate is a blockchain specialist, enthusiast, and adopter, who loves writing about complex technologies and explaining them in simple words. Kate features regularly for Liquid Loans, plus Cointelegraph, Nomics, Cryptopay, ByBit and more.

Development
Knowledge
Subscribe To Newsletter
Stay up-to-date with all the latest news about
Liquid Loans, Fetch Oracle and more.
Copyright © 2024 Crave Management.
All Rights Reserved.

The LL Librarian
Your Genius Liquid Loans Knowledge Assistant