Ethereum Sharding: The ETH Upgrade to Finally Solve The Gas Fee Problem?

Ethereum sharding is the network upgrade designed to resolve the scalability problem.
Once implemented, it will enable the Ethereum network to process a much higher number of transactions per second and, at the same time, reduce ETH gas fees.
The long-awaited solution still looms on the horizon with no exact date for implementation. Nonetheless, it is important to investigate the Ethereum sharding technology now so as to make use of it at its fullest upon release.
What is Ethereum Sharding?
Ethereum sharding refers to a scalability solution proposed for the Ethereum blockchain. It aims to improve the network's performance by dividing the blockchain into smaller pieces called shards. Each shard operates as an independent chain with its own set of smart contracts and transaction history.
The goal of sharding is to increase the throughput and capacity of the Ethereum network by allowing multiple shards to process transactions in parallel. This approach helps alleviate congestion and reduces the burden on the main Ethereum chain, also known as the "mainnet."
In a sharded Ethereum network, validators are assigned to specific shards, and they only validate transactions and execute smart contracts within their assigned shard. This parallel processing capability enables the network to handle a significantly larger number of transactions compared to the current Ethereum architecture.
The Problems of Ethereum Architecture
The Ethereum mainnet relies on a distributed network of nodes that support the network. Each Ethereum node stores information about all transactions that have ever happened within the network since its launch.
Initially, Ethereum was working on the proof of work consensus mechanism. It implies solving complex computational tasks for the new nodes to be created.
In accordance with the development roadmap, the network launched a PoS-based Beacon chain on December 1st, 2020. Finally, in September 2020, the Merge event took place as the whole network switched to PoS.
Thus, Ethereum has transferred to the proof of stake consensus and overcome the problem of excessive electricity consumption inherent to PoW-based systems. Yet, the system remained unscalable.
At the time of writing, it already features comparatively low fees and fast transaction speed. Yet, it’s still not ready to withstand high network congestion.
With the advance of Ethereum 2.0, the system should implement sharding so as to solve its last problem.
How Does Ethereum Sharding Work?

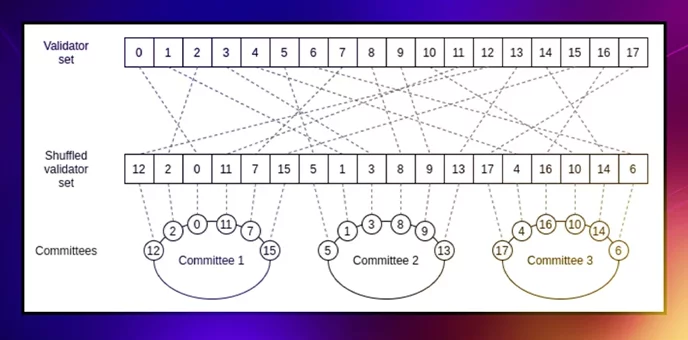
When Ethereum implements sharding, it will divide the network into smaller groups of nodes called shard chains. Each of these shards will process unique sets of transactions and then broadcast these subsets to the rest of the network.
Here’s what it’s going to look like in practice.
Assume, there are 10,000 validators who support the Ethereum network and 100 shard chains.
- In Shard 1, a validator is randomly assigned to group transactions into a subset.
- Other validators download this subset to verify the validity of transactions.
- If two-thirds of validators approve it, the subset is further broadcasted to the rest of the network.
Note that validators don’t need to verify every separate transaction on the network. To reduce the time and power needed for the verification, validator nodes only check the signatures of every group of transactions as a whole.
Advantages of Ethereum Sharding
The new approach can help to solve a number of problems inherent to the Ethereum blockchain. At this, Ethereum sharding comes with the following advantages:
- Improved scalability. The network should be able to process up to 100,000 transactions per second (TPS). In comparison with its current metrics (~13 TPS on average), this should be a real breakthrough. Besides, sharding will make it possible to process multiple functions in parallel and thus help the network scale further.
- Reduced gas fees. Sharding will also resolve another key pain of Ethereum users, i.e. high gas fees. To verify transactions, users won’t have to compete for the network resources so hard. Therefore, the fees will be much lower.
- Reduced requirements for the node holders. With sharding, every single node will no longer have to contain information about every transaction anymore. This will help to reduce the resources needed to become a validator.
- Higher decentralization. As setting up a node will be much easier, more validators will be able to join the network. The higher their number, the higher the overall decentralization, and, consequently, the higher the security of the whole system.
Disadvantages of Ethereum Sharding
While the advantages of Ethereum sharding are obvious, there are also some concerns to address as well:
- Higher complexity. Sharding makes the whole blockchain infrastructure more complex. This, in turn, increases the costs of development and makes vulnerabilities more feasible.
- A comparatively new technology. Although shading itself has been around for a while already, it is still a novelty in the blockchain industry. At this, it hasn’t been properly tested yet and, therefore, some unknown vulnerabilities may emerge in time.
- The risks of hackers hijacking separate shards. The resources needed to take over a single shard are much lower in comparison with the whole network. Thus, malicious actors may conduct a 51% attack on individual pieces of the network and submit invalid transactions to the rest of the blockchain.
How Does Ethereum Sharding Address Security Concerns?
Vitalik’s team is surely aware of all these challenges. At this, its members work on various solutions to stand against all the potential risks.
Here’s what the Ethereum roadmap includes:
- Fraud proofs. According to Vitalik’s explanation, this system pimples that only a participant with a staked deposit has a right to sign transactions. In case the signature is challenged by another participant, the deposit is lost.
- Random selection of validators. The network participants must not know in which shard they will reside as the validation committees are created randomly. Thus, it will be way more difficult for them to coordinate with each other to conduct attacks on the system.
When Will Ethereum Start Sharding (Timeline)?
Implementing sharding on top of a working blockchain is way harder than doing that from scratch.
At this, Ethereum’s team is very careful with its forecasts. The official roadmap only mentions sharding among potential branches of development but doesn’t give any specific timeline for its implementation.
Many online resources claim that the ETH upgrade can be expected at “any time in 2023”. Yet, no one has ever announced any specific date.
So far, Ethereum’s team has remained true to its words as it moves on along the predefined roadmap. Thus, all we can do now is wait for the good news to come out.
The Bottom Line
Ethereum sharding must be implemented and must be effective in order for the Ethereum gas fees to be bearable.
In the meantime, PulseChain is launching soon as a full system state copy of Ethereum.
It will have hundreds of projects launches natively, including PulseChain, and has hundreds of thousands of users already.
Join The Leading Crypto Channel
JOINDisclaimer:Please note that nothing on this website constitutes financial advice. Whilst every effort has been made to ensure that the information provided on this website is accurate, individuals must not rely on this information to make a financial or investment decision. Before making any decision, we strongly recommend you consult a qualified professional who should take into account your specific investment objectives, financial situation and individual needs.

Kate
Kate is a blockchain specialist, enthusiast, and adopter, who loves writing about complex technologies and explaining them in simple words. Kate features regularly for Liquid Loans, plus Cointelegraph, Nomics, Cryptopay, ByBit and more.

Development
Knowledge
Subscribe To Newsletter
Stay up-to-date with all the latest news about
Liquid Loans, Fetch Oracle and more.
Copyright © 2024 Crave Management.
All Rights Reserved.

The LL Librarian
Your Genius Liquid Loans Knowledge Assistant